Thank you very much for visiting Gunter's Space Page. I hope that this site is useful and informative for you.
If you appreciate the information provided on this site, please consider supporting my work by making a simple and secure donation via PayPal. Please help to run the website and keep everything free of charge. Thank you very much.
GFO
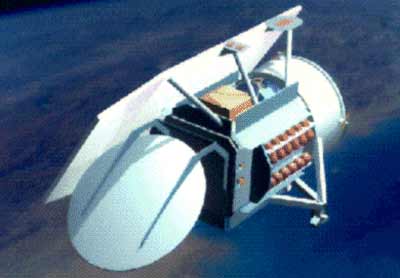
GFO [Ball]
The US Navy GFO (Geosat Follow On), is a 369 kg minisatellite based on the Techstar platform to carry on the mission of Geosat. It was launched on the 10th February 1998 on a Taurus-2210 from VAFB alongside two Orbcomm satellites, into a 789 × 881 km (779 × 790 km planned) 108 degree inclined orbit.
The missions follows the 1985 Johns Hopkins Applied Physics lab built Geosat mission. It carries a precise radar altimeter (<5 cm) to measure small changes in sea surface heights associated with ocean circulation. The altimeter was supplied by Raytheon. A microwave radiometer is also carried supplied by AIL systems Inc. The spacecraft has 96Mbytes of on-board storage, and will generate up to 126W orbit average power. Ball Aerospace built the spacecraft, which has a contractual mission lifetime of 5 years, a mission design lifetime of 8 years. The spacecraft cost was US$ 46m and the contract was awarded in 1992.
GFO operated for nearly 11 years until 2008. A follow-on mission, GFO-2, was planned to be launched in 2014, but procurement of the satellite was deferred until 2016.
| Nation: | USA |
|---|---|
| Type / Application: | Altimetry |
| Operator: | US Navy |
| Contractors: | Ball Aerospace |
| Equipment: | Radio altimeter, microwave radiometer |
| Configuration: | BCP-600 (formerly called Techstar) |
| Propulsion: | ? |
| Power: | Solar array, batteries |
| Lifetime: | 5 years planned, 10 years reached |
| Mass: | 410 kg |
| Orbit: | 775 km × 878 km, 108° |
| Satellite | COSPAR | Date | LS | Launch Vehicle | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFO | 1998-007A | 10.02.1998 | Va 576E | Taurus-2210 | with Orbcomm FM3, FM4, Celestis 03 |
References:
- Ball Aerospace: GFO
